 |
Kentucky Administrative Regulations (Last Updated: August 1, 2016) |
 |
TITLE 401. ENERGY AND ENVIRONMENT CABINET - DEPARTMENT FOR ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION |
 |
Chapter 59. New Source Standards |
401 KAR 59:015. New indirect heat exchangers
-
Section 1. Definitions. (1) "Affected facility" means an indirect heat exchanger having a heat input capacity greater than one (1) million BTU per hour (MMBTU/hr).
(2) "CEMS" means continuous emissions monitoring system.
(3) "Classification date" means:
(a) August 17, 1971, for an affected facility with a capacity greater than 250 (MMBTU/hr) heat input:
1. For particulate emissions;
2. For sulfur dioxide emissions; and
3. For nitrogen oxide emissions if fuels other than lignite are burned;
(b) April 9, 1972, for an affected facility with a capacity of 250 MMBTU/hr heat input or less for particulate emissions and sulfur dioxide emissions; and
(c) December 22, 1976, for an affected facility with a capacity greater than 250 MMBTU/hr heat input for nitrogen oxides if lignite fuel is burned.
(4) "COMS" means continuous monitoring system for opacity.
(5) "Indirect heat exchanger" means a piece of equipment, apparatus, or contrivance used for the combustion of fuel in which the energy produced is transferred to its point of usage through a medium that does not come in contact with or add to the products of combustion.
(6) "PM CEMS" means a particulate matter continuous emissions monitoring system.
Section 2. Applicability. (1) This administrative regulation shall apply to affected facilities commenced on or after the applicable classification date.
(2) An affected facility subject to 40 C.F.R. 60.40 to 60.46 (Subpart D); 60.40Da to 60.52Da (Subpart Da); 60.40b to 60.49b (Subpart Db); or 60.40c to 60.48c (Subpart Dc) shall be exempt from this administrative regulation for each pollutant covered under this administrative regulation with a specific emission standard in the applicable New Source Performance Standard (NSPS) codified at 40 C.F.R. Part 60.
Section 3. Method for Determining Allowable Emission Rates. (1) Except as provided in subsection (3) of this section, the total rated heat input capacity of all affected facilities at a source, including those for which an application to construct, modify, or reconstruct has been submitted to the cabinet, shall be used as specified in Sections 4 and 5 of this administrative regulation to determine the allowable emission rate in terms of pounds per million BTU (lb/MMBTU) heat input.
(2) The permitted allowable emissions rate of an affected facility shall not be changed due to inclusion or shutdown of another affected facility at the source.
(3) Sources may petition the cabinet to approve an allowable emission rate apportioned independently from individual heat input pursuant to this subsection, as follows:
(a) The following equation shall be used to determine the allowable emissions rate: F=(AB+DE)/C, in which:
1. A = allowable emission rate (in lb/MMBTU heat input) determined pursuant to subsection (1) of this section;
2. B = total rated heat input (in MMBTU/hr) of all affected facilities at the source commenced on or after the applicable classification date, including those for which an application to construct, modify, or reconstruct has been submitted to the cabinet;
3. C = total rated heat input (in MMBTU/hr of all affected facilities at the source, including those for which an application to construct, modify, or reconstruct has been submitted to the cabinet;
4. D = allowable emission rate (in lb/MMBTU heat input) determined pursuant to 401 KAR 61:015, Section 3(1);
5. E = total rated heat input (in MMBTU/hr) of all affected facilities at the source commenced before the applicable classification date; and
6. F = alternate allowable emission rate in lbs per actual MMBTU heat input;
(b) The total emissions (in lb/hr) from all affected facilities at the source subject to this administrative regulation divided by the total actual heat input (in MMBTU/hr) of the affected facilities shall not exceed the alternate allowable emission rate as determined in paragraph (a) of this subsection;
(c) A source operating an affected facility that is not subject to a federal NSPS codified at 40 C.F.R. Part 60 only because the affected facility commenced construction prior to the NSPS classification date, shall not allow emissions of the affected facility to exceed the allowable emission rate determined pursuant to Sections 4 and 5 of this administrative regulation;
(d) The source shall demonstrate compliance with this subsection by conducting a performance test pursuant to 401 KAR 50:045 for each affected facility subject to this administrative regulation; and
(e) The source shall demonstrate that compliance with this subsection shall be maintained on a continual basis.
Section 4. Standard for Particulate Matter. Except as provided in Section 3(3) of this administrative regulation, an affected facility subject to this administrative regulation shall not cause emissions of particulate matter in excess of:
(1)(a) 0.56 lb/MMBTU actual heat input for sources with total heat input capacity totaling ten (10) MMBTU/hr or less for all affected facilities at the source;
(b) 0.10 lb/MMBTU actual heat input for sources with total heat input capacity totaling 250 MMBTU/hr or more for all affected facilities at the source; and
(c) 0.9634 multiplied by the quantity obtained by raising the total heat input capacity (in MMBTU/hr) to the -0.2356 power for sources with heat input values totaling greater than ten (10) MMBTU/hr and less than 250 MMBTU/hr for all affected facilities at the source; and
(2) Twenty (20) percent opacity except:
(a) For sources with heat input capacity totaling 250 MMBTU/hr or more for all affected facilities at the source, a maximum of twenty-seven (27) percent opacity shall be allowed for one (1) six (6) minute period in any sixty (60) consecutive minutes;
(b) For sources with total heat input capacity of less than 250 MMBTU/hr for all affected facilities at the source, a maximum of forty (40) percent opacity shall be allowed for a maximum of six (6) consecutive minutes in any sixty (60) consecutive minutes during fire box cleaning or soot blowing; and
(c) For emissions from an affected facility caused by building a new fire, emissions during the period required to bring the boiler up to operating conditions shall be allowed, if the method used is recommended by the manufacturer and the time does not exceed the manufacturer's recommendations.
Section 5. Standard for Sulfur Dioxide. (1) Except as provided in Section 3(3) of this administrative regulation, an affected facility subject to this administrative regulation shall not cause emissions of gases that contain sulfur dioxide in excess of:
(a) For sources with heat input capacity totaling ten (10) MMBTU/hr or less for all affected facilities at the source:
1. Three and zero-tenths (3.0) lb/MMBTU actual heat input for combustion of liquid and gaseous fuels; and
2. Five and zero-tenths (5.0) lb/MMBTU actual heat input for combustion of solid fuels;
(b) For sources with heat input capacity totaling 250 MMBTU/hr or more for all affected facilities at the source:
1. Eight-tenths (0.8) lb/MMBTU actual heat input for combustion of liquid and gaseous fuels; and
2. One and two-tenths (1.2) lb/MMBTU actual heat input for combustion of solid fuels; and
(c) For sources with total heat input values greater than ten (10) MMBTU/hr and less than 250 MMBTU/hr for all affected facilities at the source, the standard, in lb/MMBTU actual heat input, shall be equal to:
1. The value 7.7223 multiplied by the quantity obtained by raising to the -0.4106 power the total heat input capacity (in MMBTU/hr) of the affected facilities combusting liquid fuels;
2. The value 7.7223 multiplied by the quantity obtained by raising to the -0.4106 power the total heat input capacity (in MMBTU/hr) of the affected facilities combusting gaseous fuels; and
3. The value 13.8781 multiplied by the quantity obtained by raising to the -0.4434 power the total heat input capacity (in MMBTU/hr) of the affected facilities combusting solid fuels.
(2) For simultaneously burning different fuels in combination, the applicable standard shall be determined by prorating BTUs pursuant to the following equation: Allowable sulfur dioxide emission in lb/MMBTU/hr heat input = {y(a) + z(b)}/(y + z), in which:
(a) y = percent total heat input derived from liquid or gaseous fuel;
(b) z = percent total heat input derived from solid fuel;
(c) a = allowable sulfur dioxide emission in lb/MMBTU/hr heat input derived from liquid or gaseous fuel; and
(d) b = allowable sulfur dioxide emission in lb/MMBTU/hr heat input derived from solid fuel.
(3) Compliance shall be based on the total heat input from all fuels burned.
Section 6. Standard for Nitrogen Oxides. (1) An affected facility with heat input capacity of 250 MMBTU/hr or more shall not cause emissions of gases that contain nitrogen oxides expressed as nitrogen dioxide in excess of:
(a) 0.20 lb/MMBTU heat input (0.36 grams per million calories (g/MMCal)) derived from gaseous fuel;
(b) 0.30 lb/MMBTU heat input (0.54 g/MMCal) derived from liquid fuel;
(c) 0.70 lb/MMBTU heat input (1.26g/MMCal) derived from solid fuel except lignite;
(d) 0.60 lb/MMBTU heat input (1.08 g/MMCal) derived from lignite or lignite and wood residue except as provided in paragraph (e) of this subsection; and
(e) 0.80 lb/MMBTU derived from lignite that is mined in North Dakota, South Dakota, or Montana and that is burned in a cyclone-fired unit.
(2) Except as provided in subsections (3) and (4) of this section, if different fuels are burned simultaneously in any combination, the allowable nitrogen dioxide emission shall be prorated using the following equation: Allowable nitrogen dioxide emission in lb/MMBTU/hr heat input {x(0.20) + y(0.30) + w(0.60)} + {(x+y+z+w)}which:
(a) x = percent of total heat input derived from gaseous fuel;
(b) y = percent of total heat input derived from liquid fuel;
(c) z = percent of total heat input derived from solid fuel (except lignite); and
(d) w = percent of total heat input derived from lignite.
(3) For fossil fuel containing at least twenty-five (25) percent by weight coal refuse burned in combination with gaseous, liquid, or other solid fossil fuel; wood residue; or biomass, the standard for nitrogen oxides shall not apply.
(4) A cyclone-fired unit burning fuel containing at least twenty-five (25) percent lignite mined in North Dakota, South Dakota, or Montana shall be subject to subsection (1)(e) of this section for all types of fuel combusted in combination with the lignite.
Section 7. Emission and Fuel Monitoring.
(1) Except as provided in subsection (2) of this section, sources shall install, calibrate, maintain, and operate a continuous monitoring system for measuring:
(a) Opacity of emissions;
(b) Sulfur dioxide emissions;
(c) Nitrogen oxides emissions; and
(d) Oxygen or carbon dioxide emissions.
(2) Subsection (1) of this section shall not apply as follows:
(a) For an affected facility burning only gaseous fuel, a continuous monitoring system for opacity (COMS) shall not be required.
(b) For an affected facility burning only natural gas, wood, wood residue, or biomass; or a combination of natural gas, wood, wood residue, or biomass, a continuous emissions monitoring system (CEMS) for sulfur dioxide emissions shall not be required.
(c)1. For nitrogen oxides, installation of CEMS may be delayed until after the initial performance tests required by 401 KAR 59:005, Sections 2 and 4(2); and
2. If the initial performance test results show nitrogen oxide emissions:
a. Are less than seventy (70) percent of the applicable standard in Section 6 of this administrative regulation, CEMS for nitrogen oxides shall not be required; or
b. Are equal to or greater than seventy (70) percent of the applicable standard in Section 6 of this administrative regulation, the source shall install CEMS for nitrogen oxides within one (1) year after the date of the initial performance tests.
(d) For a source exempt from installing CEMS for sulfur oxides and nitrogen oxides pursuant to paragraphs (b) and (c) of this subsection, a continuous monitoring system for measuring oxygen or carbon dioxide shall not be required.
(e) For an affected facility not using a flue gas desulfurization device, CEMS for sulfur dioxide emissions shall not be required if the source monitors sulfur dioxide emissions by fuel sampling and analysis pursuant to subsection (5) of this section.
(3) For performance evaluations subject to 401 KAR 59:005, Section 4(3), and calibration checks subject to 401 KAR 59:005, Section 4(4):
(a) Reference Methods 6-6C or 7-7E, incorporated by reference in 401 KAR 50:015, as applicable, shall be used for conducting performance evaluations of CEMS for sulfur dioxide and nitrogen oxides;
(b) Sulfur dioxide or nitric oxide, as applicable, shall be used for preparing calibration gas mixtures pursuant to 40 C.F.R. Part 60, Appendix B, Performance Specification 2;
(c) The span value for a continuous monitoring system:
1. For an affected facility burning fossil fuels, shall be eighty (80), ninety (90), or 100 percent; and
2. For systems measuring sulfur oxides or nitrogen oxides, shall be determined pursuant to the following table:
DETERMINATION OF SPAN VALUE
(in parts per million)
Fossil Fuel
Span Value for
Sulfur Dioxide
Span Value for
Nitrogen Oxides
Gas
*
500
Liquid
1,000
500
Solid
1,500
500
Combinations
1,000y + 1,500z
500(x + y) + 1,000z
In which:
a. * shall indicate that a value shall not be applicable;
b. x = fraction of total heat input derived from gaseous fossil fuel;
c. y = fraction of total heat input derived from liquid fossil fuel; and
d. z = fraction of total heat input derived from solid fossil fuel;
(d) Span values computed pursuant to paragraph (c) of this subsection for burning combinations of fuels shall be rounded to the nearest 500 parts per million (ppm); and
(e) The source shall submit the proposed CEMS span value for cabinet approval pursuant to 40 C.F.R. 60.13(d) and this subsection, for all affected facilities that simultaneously burn fossil fuel and nonfossil fuel.
(4) For continuous monitoring systems installed pursuant to subsection (1) of this section, the following conversion procedures shall be used to convert the continuous monitoring data into units of the applicable requirement in nanograms/joule (ng/J) or lb/MMBTU:
(a) For continuous monitoring systems measuring oxygen, the pollutant concentration and oxygen concentration shall be measured on a consistent wet or dry basis as follows:
1. Procedures approved by the cabinet and the U. S. EPA pursuant to 40 C.F.R. Part 60, Appendix B, shall be used for wet-basis measurements; and
2. For dry-basis measurements, the following conversion procedure shall be used:
E = (20.9CF)/(20.9 – percent oxygen) in which E, C, F, and percent oxygen shall be determined pursuant to subsection (5) of this section; and
(b) For continuous monitoring systems measuring carbon dioxide, the pollutant concentration and carbon dioxide concentration shall be measured on a consistent wet or dry basis and the following conversion procedure shall be used: E = (100 CFc)/(percent carbon dioxide), in which E, C, Fc, and percent carbon dioxide shall be determined pursuant to subsection (5) of this section.
(5) The values used in the equations in subsection (4)(a) and (b) of this section shall be derived as follows:
(a) E = pollutant emissions in grams per million calorie (g/MMCal) or lb/MMBTU;
(b) C = pollutant concentration in grams per dry cubic meter at standard conditions (g/dscm) or pounds per dry cubic feet at standard conditions (lb/dscf) determined by multiplying the average concentration (ppm) for each one (1) hour period by 0.0000415 M (g/dscm)/ppm or (lb/dscf)/ppm; multiplied by two and five-tenths (2.5) multiplied by ten (10) raised to the negative ninth (9) power; and multiplied by M (g/dscm)/ppm or (lb/dscf)/ppm in which M equals:
1. Pollutant molecular weight in grams per gram-mole (g/g-mole) or pounds/pound-mole (lb/lb-mole); or
2. 64.07 for sulfur dioxide and 46.01 for nitrogen oxides;
(c) F, Fc = a factor representing a ratio of the volume of dry flue gases generated to the calorific value of the fuel combusted (F), and a factor representing a ratio of the volume of carbon dioxide generated to the calorific value of the fuel combusted (Fc), respectively, pursuant to the applicable American Society for Testing and Materials (ASTM) standard from the Book of ASTM Standards incorporated by reference in 401 KAR 50:015 as follows:
1. For anthracite coal as classified according to ASTM D388-66(72), F equals 10,140 dscf/MMBTU and Fc equals 1,980 standard cubic feet (scf) CO2/MMBTU;
2. For subbituminous and bituminous coal as classified according to ASTM D388-66(72), F equals 9,820 dscf/MMBTU and Fc equals 1,810 scf CO2/MMBTU;
3. For liquid fossil fuels including crude, residual, and distillate oils, F equals 9,220 dscf/MMBTU and Fc equals 1,430 scf CO2/MMBTU;
4a. For gaseous fossil fuels, F equals 8,740 dscf/MMBTU;
b. For natural gas, Fc equals 1,040 scf CO2/MMBTU; for propane, Fc equals 1,200 scf CO2/MMBTU; and for butane Fc equals 1,260 scf CO2/MMBTU;
5a. For bark, F equals 9,575 dscf/MMBTU and Fc equals 1,927 scf CO2/MMBTU;
b. For wood residue other than bark, F equals 9,233 dscf/MMBTU, and Fc equals 1,842 scf CO2/MMBTU; and
6. For lignite coal as classified according to ASTM D388-66(72), F equals 9,900 dscf/MMBTU and Fc equals 1,920 scf CO2/MMBTU;
(d) The source may use the equation given in subparagraph 1 of this paragraph to determine an F factor (dscm/MMCal, or dscf/MMBTU) on a dry basis or Fc factor (standard cubic meters (scm) CO2/MMCal, or standard cubic feet (scf) CO2/MMBTU) on either wet or dry basis in lieu of the F or Fc factors specified in paragraph (c) of this subsection; where
1. The F or Fc Factor shall be determined by the following:
a. F = {227.2 (%H) + 95.5 (%C) + 35.6 (%S) +8.7 (%N) - 28.7 (%O)} / GCV (metric units);
b. F = 106 {3.64 (%H) + 1.53 (%C) + 0.57 (%S) + 0.14 (%N) - 0.46 (%O)} / GCV (English units);
c. Fc = {2.0 x 10-5 (%C)} / GCV (metric units); and
d. Fc = {3.21 x 105 (%C)} / GCV (English units);
2. H, C, S, N, and O shall be content by weight of hydrogen, carbon, sulfur, nitrogen, and oxygen (expressed as percent), respectively, as determined on the same basis as GCV by ultimate analysis of the fuel fired using ASTM method D3178-73 or D3176-74 (solid fuels) or computed from results using ASTM methods D1137-53(75), D1945-64(73), or D1946-67(72) (gaseous fuels) as applicable; and
3. GCV shall be the gross calorific value (Cal/g or BTU/lb) of the fuel combusted determined by ASTM test methods D2015-66(72) for solid fuels and D1826-64(70) for gaseous fuels as applicable; and
(e) For an affected facility firing a combination of fuels, the F or Fc factors determined by paragraphs (c) and (d) of this subsection shall be prorated in accordance with the applicable formula as follows:
1. F = xF1 + yF2 + zF3, where:
a. x, y, z = the fraction of total heat input derived from gaseous, liquid, and solid fuels, respectively; and
b. F1, F2, F3 = the value of F for gaseous, liquid, and solid fuels, respectively, pursuant to subsection (5)(c) and (d) of this section; or
2.
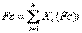
where:
a. Xi = fraction of total heat input derived from each type fuel; and
b. (Fc)i = applicable Fc factor for each fuel type determined pursuant to subsection (5)(c) and (d) of this section.
(6) For reports required pursuant to 401 KAR 59:005, Section 3(3), periods of excess emissions required to be reported shall be as follows:
(a) Excess emissions shall be any six (6) minute period during which the average opacity of emissions exceeds twenty (20) percent opacity, except that one (1) six (6) minute average per hour of up to twenty-seven (27) percent opacity shall not be required to be reported;
(b) For sulfur dioxide, excess emissions shall be any three (3) hour period during which the average emissions (arithmetic average of three (3) contiguous one (1) hour periods) of sulfur dioxide as measured by a continuous monitoring system exceed an applicable standard in Section 5 of this administrative regulation; and
(c) For nitrogen oxides, excess emissions shall be any three (3) hour period during which the average emissions (arithmetic average of three (3) contiguous one (1) hour periods) of nitrogen oxides as measured by a continuous monitoring system exceed an applicable standard in Section 6 of this administrative regulation.
(7) The source may request approval to install a Particulate Matter Continuous Emissions Monitoring System (PM CEMS) as an alternative to subsection (1)(a) of this section as follows:
(a) The request for approval shall be made in writing to the cabinet;
(b) if the PM CEMS request is approved, the source:
1. Shall be subject to a federally enforceable PM limit of 0.030 lb/MMBTU/hr or less;
2. Shall comply with 40 C.F.R. 60.42Da(a); and
3. Shall follow the compliance and monitoring provisions of 40 C.F.R. 60.48Da and 60.49Da that are applicable to particulate matter, excluding 40 C.F.R. 60.48Da(c) and (g)(3);
(c) Excess emissions for an affected facility using PM CEMS shall be determined by a boiler-operating-day, as defined by 40 C.F.R. 60.41Da, in which the average emissions (arithmetic average of all operating one (1) hour periods) exceed the applicable standard pursuant to 40 C.F.R. 60.42Da; and
(d) For calculating average emissions and determining compliance:
1. The boiler operating day shall have at least eighteen (18) hours of unit operation during which the standard shall apply; and
2. All valid hourly emission rates of the boiler operating day not meeting the minimum eighteen (18) hours valid data daily average requirement shall be averaged with the valid hourly emission rates of the next boiler operating day with eighteen (18) hours or more of valid PM CEMS data.
Section 8. Test Methods and Procedures. (1) Except as provided in 401 KAR 50:045, the reference methods specified in 40 C.F.R. Part 60, Appendix A shall be used to determine compliance with Sections 4, 5, and 6 of this administrative regulation as follows:
(a) Reference Method 1 shall be used for the selection of sampling site and sample traverses;
(b) Reference Method 3 shall be used for gas analysis in applying Reference Methods 5, 6, and 7;
(c) Reference Method 5 shall be used for concentration of particulate matter and the associated moisture content;
(d) Reference Method 6 shall be used for the concentration of sulfur dioxide;
(e) Reference Method 7 shall be used for the concentration of nitrogen oxides; and
(f) Reference Method 9 shall be used for visible emissions.
(2) For Reference Method 5:
(a) Reference Method 1 shall be used to select the sampling site and the number of traverse sampling points;
(b) The sampling time for each run shall be at least sixty (60) minutes, and the minimum sampling volume shall be 0.85 dscm (thirty (30) dscf) except smaller sampling times or volumes, if necessitated by process variables or other factors, may be requested by the source; and
(c) The probe and filter holder heating systems in the sampling train shall be set to provide a gas temperature not greater than 160 degrees Centigrade (320 degrees Fahrenheit).
(3) For Reference Methods 6 and 7:
(a) The sampling site shall be the same as the site selected for Reference Method 5;
(b) The sampling point in the duct shall be at the centroid of the cross section or at a point no closer to the walls than one (1) meter (3.28 ft); and
(c) For Reference Method 6, the sample shall be extracted at a rate proportional to the gas velocity at the sampling point.
(4) For Reference Method 6:
(a) The minimum sampling time shall be twenty (20) minutes, and the minimum sampling volume shall be 0.02 dscm (0.71 dscf) for each sample;
(b) The arithmetic mean of two (2) samples shall constitute one (1) run; and
(c) Samples shall be taken at approximately thirty (30) minute intervals.
(5) For Reference Method 7:
(a) Each run shall consist of at least four (4) grab samples taken at approximately fifteen (15) minute intervals; and
(b) The arithmetic mean of the samples shall constitute the run value.
(6) For each run using the methods specified by subsection (1)(a), (b), and (c) of this section, the emissions expressed in g/MMCal (lb/MMBTU) shall be determined by the following procedure:
E = 20.9CF/(20.9-percent oxygen), in which:
(a) E = pollutant emission, g/MMCal (lb/MMBTU);
(b) C = pollutant concentration, g/dscm (lb/dscf), determined by Reference Methods 5, 6, or 7;
(c) Percent oxygen:
1. Shall equal oxygen content by volume (expressed as percent), dry basis; and
2. Shall be determined using the integrated or grab sampling and analysis procedures of Reference Method 3:
a. For determination of sulfur dioxide and nitrogen oxides emissions, the oxygen sample shall be obtained simultaneously at the same point in the duct as used to obtain the samples for Reference Methods 6 and 7 determinations, respectively, with the oxygen sample for reference Method 7 obtained using the grab sampling and analysis procedures of Reference Method 3; and
b. For determination of particulate emissions, the oxygen sample shall be obtained simultaneously by traversing the duct at the same sampling location used for each run of Reference Method 5 pursuant to subsection (2) of this section, using Reference Method 1 for selection of the number of traverse points except that not more than twelve (12) points shall be required; and
(d) F = a factor as determined in Section 7(5) of this administrative regulation.
(7) If an affected facility fires a combination of fossil fuels, the heat input, expressed in Cal/hr (BTU/hr), shall be determined during each testing period by multiplying the gross calorific value of each fuel fired by the rate of each fuel burned, in which:
(a) Gross calorific value shall be determined in accordance with ASTM methods D2015-66(72) (solid fuels), D240-76 (liquid fuels), or D1826-64(70) (gaseous fuels) as applicable; and
(b) The rate of fuels burned during each testing period shall be determined by the applicable method and shall be confirmed by a material balance over the steam generation system. (5 Ky.R. 406; Am. 1023; eff. 6-6-79; 7 Ky.R. 227; 456; eff. 1-7-81; TAm eff. 8-9-2007; 35 Ky.R. 1253; 1787; 2044; eff. 4-3-09; 37 Ky.R. 957; 10-7-2010.)
Notation
RELATES TO: KRS 224.10, 40 C.F.R. Part 60, Appendices A and B
STATUTORY AUTHORITY: KRS 224.10-100(5)
NECESSITY, FUNCTION, AND CONFORMITY: KRS 224.10-100(5) requires the cabinet to promulgate administrative regulations for the prevention, abatement, and control of air pollution. This administrative regulation provides for the control of emissions from new indirect heat exchangers.